Introduction
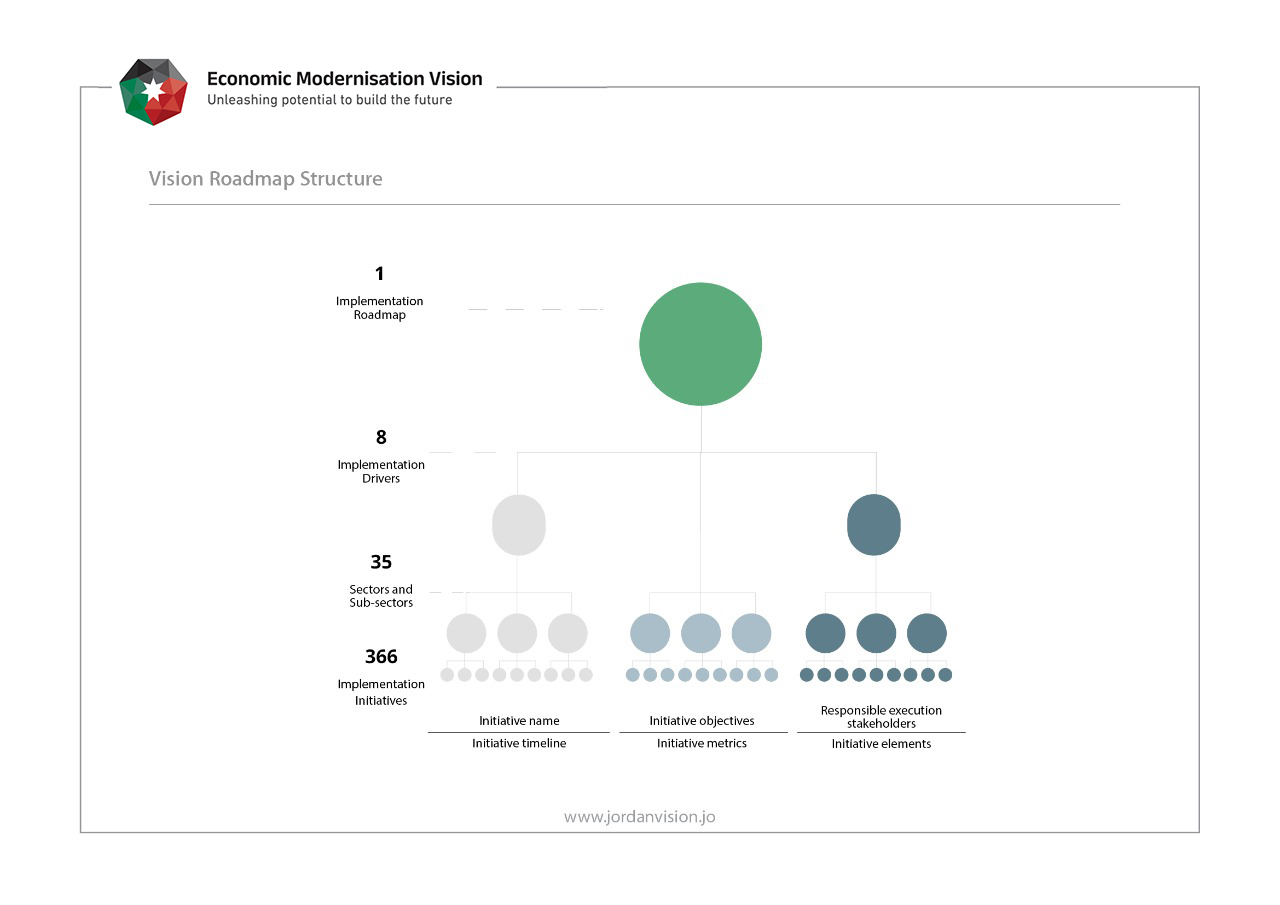
The implementation roadmap includes comprehensive and various actionable initiatives, which have been identified throughout the sectoral economic workshops, with a particular focus on the period 2022-2025.
At the heart of the roadmap are eight drivers that will lead the implementation. Each driver is broken down into specific sectors to action the implementation. In total, there are 35 sectors and sub-sectors and over 300 initiatives. Each initiative is mapped into an initiative card containing the initiative objectives, stakeholders subdivided into initiative owners and participants, a timeline with specific start and end points, initiative metrics to track the progress and delivery, and a detailed checklist of deliverables to be addressed through the implementation process, including an emphasis on unleashing women and youth’s potential across all domains.
Growth Drivers to implement the Economic Modernisation Vision
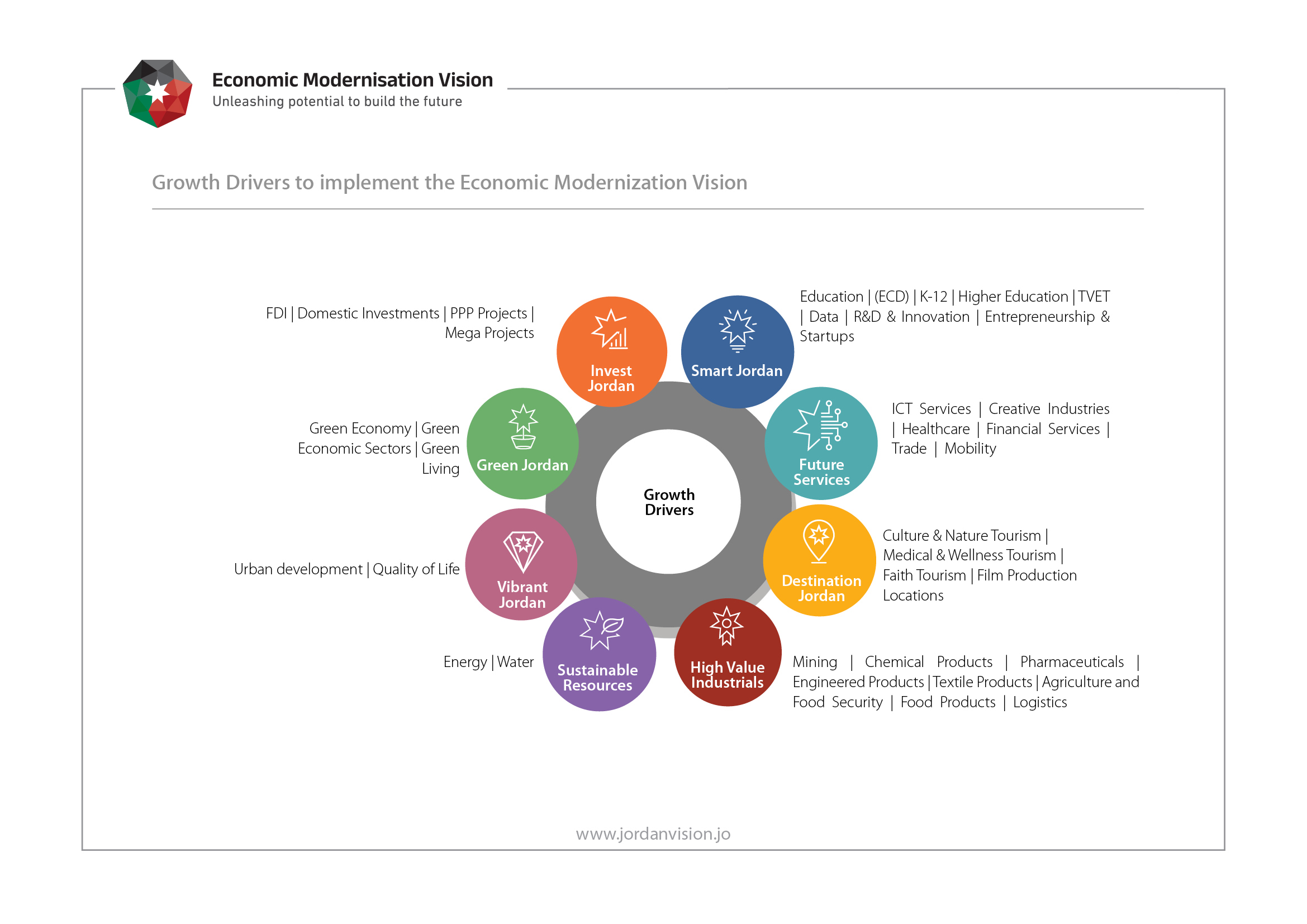
The drivers were defined by combining logically connected sectors into cohesive groupings for the purposes of organizing concerted actions. The groupings were based on three factors:
Linkages Among Sectors: logical linkages of a sector with other sectors to form value chains or growth clusters, e.g. mining with downstream chemical products manufacturing or agriculture with food processing, thus promoting the realization of synergies across the driver.
Roles of Sectors: drivers of economic growth against enablers of economic growth.
Common Sectors’ Characteristics: shared attributes among sectors; for example, a common focus on knowledge and innovation as a source of competitive advantage.
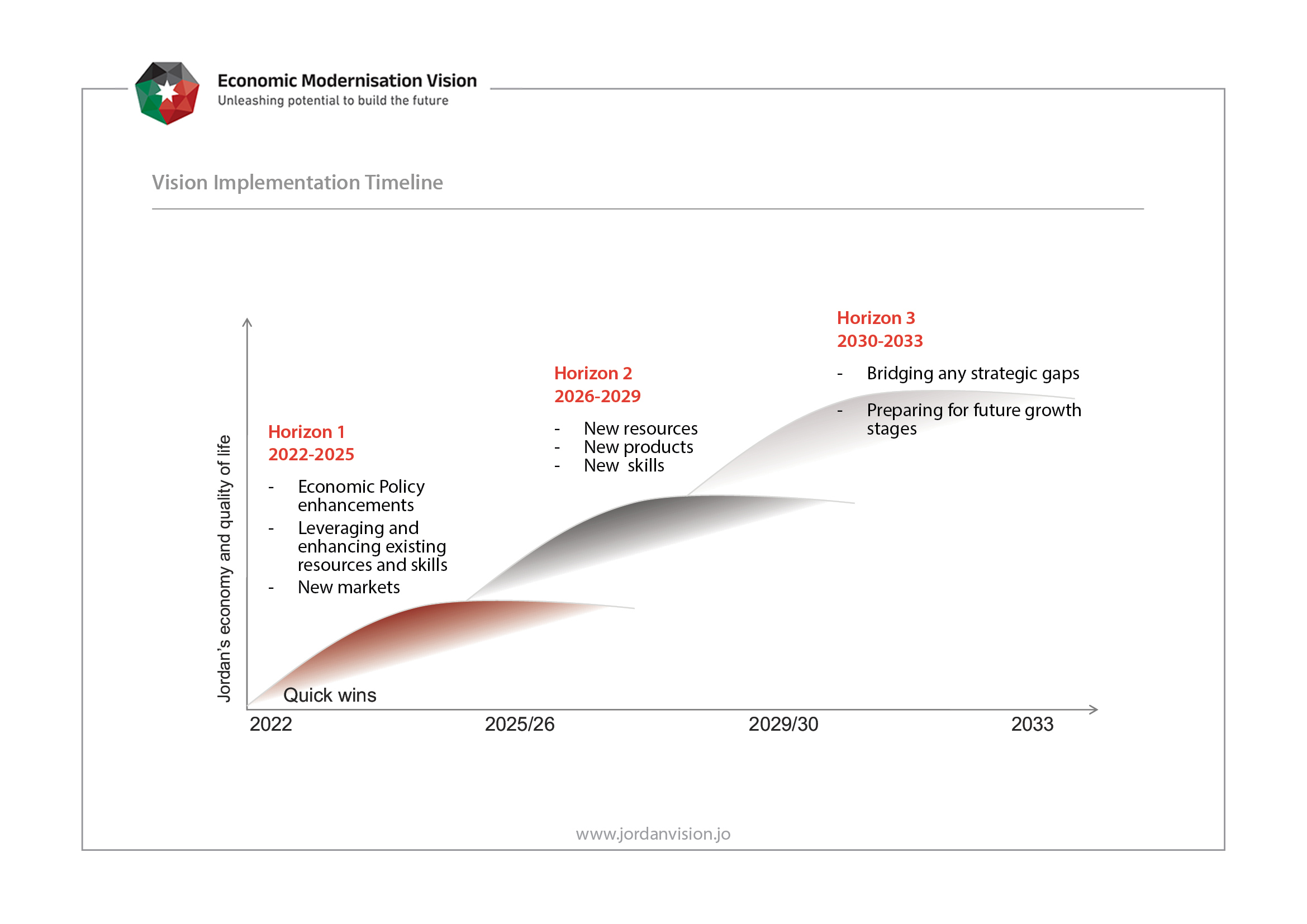
Vision Implementation Timeline
Vision Roadmap Structure
At the heart of the roadmap are eight drivers that will lead the implementation. Each driver has broken down into specific sectors to action the implementation. In total, there are 35 sectors and sub-sectors and 366 initiatives.